 The ongoing fight to contain the outbreak of COVID-19, the Coranavirus—now entering a new stage of transforming itself into a global epidemic—gives rise to recollection of another virus that swept the world just over one hundred years ago, the so-called Spanish Flu✺. For most of the rest of the 20th century, the Spanish Flu (sometimes known as La Grippe) was largely neglected by researchers and mainstream historians, and study confined to actuaries, specialist epidemiologists and virologists and medical historians [Laura Spinney, Pale Rider: The Spanish Flu of 1918 and How it Changed the World, (2017)].
The ongoing fight to contain the outbreak of COVID-19, the Coranavirus—now entering a new stage of transforming itself into a global epidemic—gives rise to recollection of another virus that swept the world just over one hundred years ago, the so-called Spanish Flu✺. For most of the rest of the 20th century, the Spanish Flu (sometimes known as La Grippe) was largely neglected by researchers and mainstream historians, and study confined to actuaries, specialist epidemiologists and virologists and medical historians [Laura Spinney, Pale Rider: The Spanish Flu of 1918 and How it Changed the World, (2017)].

(Credit: CNN International)
Why did such a devastating pandemic fly under the radar for so long? The timing of the outbreak goes a good way to explain this. After having suffered four long years of a unique world war, people tended to treat the Spanish Flu as a footnote to the Great War conflagration. Moreover, the war, concentrated in Europe and the Middle East, had a limited geographical focus for people, contrasting with the pneumonic influenza outbreak which was truly global [The Spanish Flu Pandemic’, (L Spinney), History Today, 67(4), April 2017]. As catastrophic events go, the two stand in stark contrast. With today’s scientific and medical advances experts estimate that the Spanish Flu killed at least 50 million people worldwide, some estimates put it as high as 100 million [NP Johnson & J Mueller 2002;76: 105-115 (‘Updating the accounts: Global mortality of the 1918-1920 “Spanish” Flu pandemic’, Bull Hist Med)]. Estimates of World War I casualties—military and civilian–—sit somewhere in the range of 20 to 22 million deaths [‘WW1 Casualties’, (WW1 Facts), http://ww1facts.net]⌖. By the late 20th century and early 2000s outbreaks of new viruses like SARS, Asian Bird Flu, Swine Flu, etc, spurred mainstream historians◙ to look afresh at the great global influenza of 1918-20.

An abnormal spike in morbidity and mortality
The Spanish Flu was truly global, like the Coronavirus its lethal reach touched every continent except Antartica, both are novel (new) respiratory illnesses. Similarities have been noted between the responses to the two outbreaks, eg, the issuing of instructions or recommendations by the authorities for the public to wear masks, avoid shaking hands (part of social distancing), good hygiene, quarantine, an alarmist overreaction by the media [‘Coronavirus response may draw from Spanish flu pandemic of 100 years ago’, ABC News, (Matt Bamford), 05-Mar-2020, www.amp.abc.net.au]. The great flu of 1918’s morbidity and mortality rates were frighteningly high and far-reaching…one in three people on earth were affected by it✪. Between 2.5 and 5% of the world’s population perished, including India a mind-boggling 17M-plus, Dutch East Indies 1.5M, US (up to) 675,000◍, Britain 250,000, France 400,000, Persia (Iran) (up to) 2.4M, Japan 390,000-plus, Ghana (at least) 100,000, Brazil 300,000, USSR (unknown, but conservatively, greater than 500,000)⊞.
While densely crowded communities were thought the biggest risk of mass infection, the Flu caused human devastation even in remote, isolated corners of the world, eg, in Oceania, Samoa bereft of immunity, lost 22% of its population in two months, the Fijian islands lost 14% in a 16-day period⌀. The kill rate was something around 2.5% cf. a ‘normal’ flu outbreak a rate of no more than 0.1% would be expected [‘The Spanish Flu Pandemic’, (Spinney, History Today ; ‘The Spanish Flu’, Wikipedia, http://en.m.wikipedia.org/]. (Source: National Library of Australia)
(Source: National Library of Australia)
If the Spanish Flu didn’t originate in Spain, where did it originate?
No one knows for sure is the short answer…but there has been much speculation on the topic. At the time of the epidemic a popular notion was that the Flu started in China, but China experienced low rates of infection compared to other regions of the world. The explanation for this perhaps lay in that China was subjected to an initial, mild flu season which gave its citizens an acquired immunity to the disease when the more severe strain of the virus hit them.

🔺 Red Cross volunteers: caring for the sick during the Spanish Flu fell overwhelmingly on women (volunteers and professional nurses) who bore the brunt of the work at quarantine stations and camps, as well as exposing themselves to great personal risk
🔻 Influenza-ravaged Ft Riley soldiers in hospital camp 
The military, mobility and zoonosis
Another theory attributes the Spanish Flu’s beginnings to the movements of the combatants in WWI. Virologist John Oxford favours the village of Étaples in France as the centre of the 1918 influenza infection. From a hospital camp here, 10,000 troops passed through every day…with their immune systems weakened by malnourishment and the stresses of battle and chemical attacks they were susceptible to the disease which was probably transmitted via a piggery and poultry on the same site. Once contracted, it’s dissemination was likely facilitated by mass transportation of troops by train.
Another view that has gained wide currency locates the Flu’s genesis in America’s Midwest. In recent times, historians led by Alfred W Crosby have supported the view that the epidemic started not in Europe but in a US Army base in Kansas in 1917 (America’s Forgotten Pandemic). According to adherents of this theory soldiers training at Fort Riley for combat in Europe contracted the H1N1 influenza virus which had mutated from pigs. The infected troops, they contend, then spread the virus via the war on the Western Front. Whether or not the virus started with WWI fighting men in France or in the US, it is undeniable that the soldiers moving around in trains and sailors in ships were agents of the Flu’s rapid dissemination [‘Spanish Flu’, History Today, (Upd. 05-Feb-2020), www.historytoday.com]. A recent, alternative origin view by molecular pathologist Jeffrey Taubenberger rejects the porcine transference explanation. Based on tests he did on exhumed victim tissue, Taubenberger contends that the epidemic was the result of bird-to-human transmission [‘Spanish flu: the killer that still stalks us, 100 years on’, (Mark Honigsbaum), The Guardian, 09-Sep-2018, www.theguardian.com].
(Image credit: Guia turístico)
Demographics: differential age groups
The pattern of Coronavirus mortality points to the disease being most virulent and most fatal to elderly people (the seventies to the nineties age group). This accords with most flu season deaths, although unlike seasonal flu outbreaks Coronavirus contagion has (thus far) had minimal impact on children, in particular the under-fives (Honigsbaum). But the pattern of Spanish Flu was markedly different, the records show a targeting of young adults, eg, in the US 99% of fatalities in 1918-19 were people under 65, with nearly 50% in the 20 to 40 age bracket (‘Spanish Flu’, Wiki). Statistics from other countries on the 1918 outbreak conform to a similar trend.

🔺 Conveying the health message to the public (Source: www.shelflife.cooklib.org)
The Flu in a series of varyingly virulent waves
The first wave of the Flu in early 1918 was relatively mild. This was followed by a second, killer wave in August. This mutated strain was especially virulent in three disparate places on the globe, Brest in France, Freetown in Sierra Leone and Boston in the US. There were myriad victims, some died (quickly) because they had not been exposed to the first, milder wave which prevented them from building up immunity to this more powerful strain [‘Four lessons the Spanish flu can teach us about coronavirus’ (Hannah Devlin), The Guardian, 04-Mar-2020, www.msn.com]. The second wave was a global pathogen sui generis. The bulk of the deaths occurred in a 13-week period (September to December). The lethality of the disease, and especially the speed with which it progressed, was the scariest part✧.
 2nd wave curve in the US, 1918: note the different mortality peaks during Oct-Dec 1918 for St Louis (imposed a stringent lockdown) vs Philadelphia (much less restrictive approach)
2nd wave curve in the US, 1918: note the different mortality peaks during Oct-Dec 1918 for St Louis (imposed a stringent lockdown) vs Philadelphia (much less restrictive approach)
(Source: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2007)
The symptoms of this murderously effective strain were unusual and extreme, eg, haemorrhaging from mucous membranes, bleeding from the eyes, ears and orifices, etc. The extreme severity of the symptoms were thought to be caused by cytokine storms (overreaction of the body’s immune system) (‘Spanish Flu’, Wiki) [‘Spanish Flu’, History, 12-Oct-2010, www.history.com]. The third and last strain of the Flu, in 1919, was markedly milder by comparison to the second, but still more intense than the first.
Many parallels exist between the 1918 flu outbreak and the present pandemic – of a positive nature, the widespread advocacy of wearing masks to limit the spread of disease and mandatory lockdowns. Plenty of negative parallels too – the disregarding of science and medical expertise on how to tackle the outbreak; countries engaging in playing the “blame game” against each other rather then co-operating on a united approach to the pandemic. There was especially, but not only in the US, a repetition by some of the denial at the national leadership level to square up to the pandemic and give it the complete seriousness it demanded.
✥ ⌯ ✥ ⌯ ✥
In 1919 in the middle of the flu crisis, Irish poet WB Yeats wrote in a poem the line for which he is perhaps best remembered: “Things fall apart; the centre cannot hold; mere anarchy is loosed upon the world…”
✥ ⌯ ✥ ⌯ ✥
Footnote: The health authorities’ inability to check the juggernaut of the 1918 virus was exacerbated by misdiagnosis – at it’s onset the Spanish Flu was widely believed to be a bacterium like the Black Death, not a virus. Misreading the symptoms, the influenza outbreak was variously and erroneously diagnosed as dengue, cholera or typhoid (Spinney, ‘History Today’; ‘Spanish Flu’, History).
 (Photo: State Archives & Records, NSW)
(Photo: State Archives & Records, NSW)
PostScript: The lessons of a global catastrophe
The Spanish Flu in its vast human decimation rammed home lessons for post-WWI governments and health practitioners in its wake. Being helpless to prevent or halt the virus once in full swing, the vital need to develop vaccines to counter pandemics was subsequently understood. Advanced countries started to restructure their public health systems to try to cope (such as the United States’ NIH – National Institutes of Health, which emerged about 10 years after the Spanish Flu) [‘The great influenza The epic story of the deadliest plague in history‘ (JM Barry), Reviewed by Peter Palese, (JCI), www.ncbi.nim.nih.gov]. And of course the 1918 flu virus had other, indirect, outcomes…it led to universal healthcare, alternative medicine, intensive care facilities and a modern preoccupation with the benefits of healthy exercise under clean, clear skies (‘Pale Rider’).
⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴⌴
✺ the name is a misnomer. The Spanish association came about thus: with the Great War still raging other combatant European nations such as France and Germany had imposed censorship restrictions on the reportage of the flu outbreak, whereas Spain being neutral in the war did not. When the Spanish press freely reported a serious eruption of the Flu, people outside the country unquestioningly assumed that the influenza came from Spain
⌖ to further break that down, more American troops died from the Spanish Flu than in combat during WWI (‘Pale Rider‘)
⊞ the numbers cited tend to be approximations given the paucity of adequate record-keeping at the time
◙ part of a new multidisciplinary approach to the subject including economists, sociologists and psychologists
◍ consequently life expectancy for Americans dropped by 12 years in 1918, and for the first time since Britain commenced recording data, the death-rate in 1919 exceeded the birth-rate (Honigsbaum)
✪ Pandemic: pan ⤑ all ║ demos ⤑ the people (not literally but fairly close)
⌀ although isolation did prove beneficial in some instances, such as in Australia where the virus didn’t arrive until 1919 and entry was closely monitored with a maritime quarantine program. As a result Australia’s death-rate of 2.7 per 1000 of population was one of the lowest recorded [‘Influenza pandemic’, National Museum of Australia, www.nma.gov.au]
✧ Philadelphia alone experienced 4,597 influenza deaths in a single week
 As Europe moves through Autumn, a number of countries are reporting new records for coronavirus infections. This month Italy recorded a 24-hour total of over 10,000 new cases for three consecutive days, while France recorded its highest ever total of new cases for a single day, 32,427. Similarly, the Czech Republic broke the 10,000 barrier for the first time (1,105 cases). Even in Germany, virus cases for a single day reached a pandemic high of 7,830 [‘Italy steps up coronavirus restrictions as Europe fights second wave’, Euronews, 18-Oct-2020, www.euronews.com].
As Europe moves through Autumn, a number of countries are reporting new records for coronavirus infections. This month Italy recorded a 24-hour total of over 10,000 new cases for three consecutive days, while France recorded its highest ever total of new cases for a single day, 32,427. Similarly, the Czech Republic broke the 10,000 barrier for the first time (1,105 cases). Even in Germany, virus cases for a single day reached a pandemic high of 7,830 [‘Italy steps up coronavirus restrictions as Europe fights second wave’, Euronews, 18-Oct-2020, www.euronews.com].
 (Photo: Getty Images)
(Photo: Getty Images)  (Source: www.dw.de/)
(Source: www.dw.de/)










































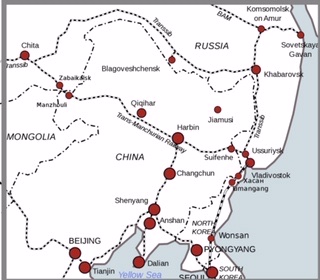 The plague was first noticed in the Inner Mongolian town of Manzhouli on the Chinese-Russian border, where Russian doctors began treating patients with fever and haemoptysis symptoms. Thus began the Great Manchurian Plague which eventually took up to 60,000 lives in less than six months – with a mortality rate very close to 100 per cent [William C Summers, The Great Manchurian Plague: The Geopolitics of an Epidemic Disease, (2012)].
The plague was first noticed in the Inner Mongolian town of Manzhouli on the Chinese-Russian border, where Russian doctors began treating patients with fever and haemoptysis symptoms. Thus began the Great Manchurian Plague which eventually took up to 60,000 lives in less than six months – with a mortality rate very close to 100 per cent [William C Summers, The Great Manchurian Plague: The Geopolitics of an Epidemic Disease, (2012)].

 In the disease’s wake mortality proceeded at an alarming rate, Harbin in the far north was the initial epicentre. In November 5,272 died in the city. It then spread along the tracks to cities further south, Mukden recorded a death toll of 2,571 by January 1911, and Changchun was losing over 200 a day to the plague (Meiklejohn). The plague was sustained and promoted by the prevailing conditions it encountered – dense population, high human mobility and poor hygiene environments (Cornelia Knab, cited in Meiklejohn). Eventually the plague reached Peking and as far as central China
In the disease’s wake mortality proceeded at an alarming rate, Harbin in the far north was the initial epicentre. In November 5,272 died in the city. It then spread along the tracks to cities further south, Mukden recorded a death toll of 2,571 by January 1911, and Changchun was losing over 200 a day to the plague (Meiklejohn). The plague was sustained and promoted by the prevailing conditions it encountered – dense population, high human mobility and poor hygiene environments (Cornelia Knab, cited in Meiklejohn). Eventually the plague reached Peking and as far as central China





































 The ongoing fight to contain the outbreak of COVID-19, the Coranavirus—now entering a new stage of transforming itself into a global epidemic—gives rise to recollection of another virus that swept the world just over one hundred years ago, the so-called Spanish Flu
The ongoing fight to contain the outbreak of COVID-19, the Coranavirus—now entering a new stage of transforming itself into a global epidemic—gives rise to recollection of another virus that swept the world just over one hundred years ago, the so-called Spanish Flu






 2nd wave curve in the US, 1918: note the different mortality peaks during Oct-Dec 1918 for St Louis (imposed a stringent lockdown) vs Philadelphia (much less restrictive approach)
2nd wave curve in the US, 1918: note the different mortality peaks during Oct-Dec 1918 for St Louis (imposed a stringent lockdown) vs Philadelphia (much less restrictive approach)