In 1910 the 265 year-old Qing Dynasty in China was fasting approaching its denouement. The following year it would be deposed and replaced with a republic. Over the years leading up to this point, Imperial China had been in long drawn-out decline, suffering a series of reversals – a disastrous defeat in the (1st) Sino-Japanese War (1894-95) and ensuing loss of territorial sovereignty in Manchuria; the crushing of the Peking Boxer Rebellion in 1900. In 1907 China had been beset by the latest (and one of the worst) of a series of famines (“Third Plague Pandemic”), losing an estimated 25 million of it’s population. And in late 1910, Manchuria in the midst of a tense political situation—China having to share the region with competing Russian and Japanese aspirations—a plague broke out.
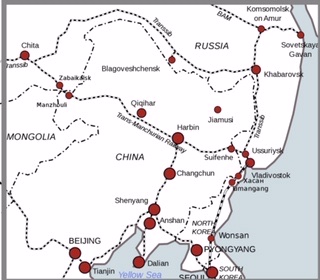 The plague was first noticed in the Inner Mongolian town of Manzhouli on the Chinese-Russian border, where Russian doctors began treating patients with fever and haemoptysis symptoms. Thus began the Great Manchurian Plague which eventually took up to 60,000 lives in less than six months – with a mortality rate very close to 100 per cent [William C Summers, The Great Manchurian Plague: The Geopolitics of an Epidemic Disease, (2012)].
The plague was first noticed in the Inner Mongolian town of Manzhouli on the Chinese-Russian border, where Russian doctors began treating patients with fever and haemoptysis symptoms. Thus began the Great Manchurian Plague which eventually took up to 60,000 lives in less than six months – with a mortality rate very close to 100 per cent [William C Summers, The Great Manchurian Plague: The Geopolitics of an Epidemic Disease, (2012)].

Vector from the rodent family
Because of a past pattern of bubonic plague in China, rats and fleas were initially suspected to be the source of human infection. 50,000 rats were examined but the results proved negative [CHERNIN, ELI. “Richard Pearson Strong and the Manchurian Epidemic of Pneumonic Plague, 1910–1911.” Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences, vol. 44, no. 3, 1989, pp. 296–319. JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/24633015. Accessed 5 May 2020]. The disease was eventually traced to the Siberian marmot (Marmota sibirica) or tarbagan, found in Inner Mongolia, eastern Siberia and Heilongjiang. Later research by Dr Wu (see below) and others established that the plague, like the present coronavirus, was pneumonic, transmitted animal to human by respiratory droplets, and not bubonic.
A roaring trade in fake mink
The European fashion for mink and ermine furs can be ‘fingered’ for being at the bottom of the preconditions leading to the 1910 plague. Mink’s popularity as one of the most prized materials for clothing accessories made it’s cost prohibitive to all but the richest Europeans. Things changed when it was discovered that the fur of the marmot when dyed passed very convincingly for mink fur. After the pelt price for marmot fur soared from 12 cents to 72 cents a hide, hordes of Chinese hunters from the central provinces swarmed into the region to join the lucrative hunt for the now in-demand creature. Mongol and Buryat hunters, long experienced in marmot-hunting knew how to select only tarbagan marmots which were not diseased for culling. The inexperienced Chinese trappers however didn’t practice safe hunting methods, failing to discern the difference, they hunted marmots indiscriminately. Thus, the infection was passed on to humans from the pelts of the disease-ridden rodents (Chernin; ‘Manchurian Plague 1910-11’, (Summers; Iain Meiklejohn), Disasterhistory.org, (April 2020), www.disasterhistory.org].

Spreading the plague by rail
Manchuria at the time was equipped with an extensive network of railroads, thanks to the vested interests of the Russians and the Japanese which the Qing Dynasty had, reluctantly, conceded. Russia controlled the Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR) and the China Eastern Railway (CER), Japan controlled the Southern Manchurian Railway (SMR)⌖. The time of the year was an important factor. From November/December, as the weather turned arctic-like, the Chinese hunters and agricultural migrant workers started to return to their home regions. The foremost consideration was to get back before the Chinese New Year. The hunters and the labourers, huddled together infecting each other in the bitter cold of the train carriages, carried the plague along the railway lines. In a short time the plague travelled from its origin point to large cities on the Dongbei line, Harbin, including the central district of Fuchiatien (Fujiandian), Changchun and Mukden (today Shenyang). Compare this to what happened with the coronavirus outbreak which spread from Wuhan to other Chinese cities by airplane.
 In the disease’s wake mortality proceeded at an alarming rate, Harbin in the far north was the initial epicentre. In November 5,272 died in the city. It then spread along the tracks to cities further south, Mukden recorded a death toll of 2,571 by January 1911, and Changchun was losing over 200 a day to the plague (Meiklejohn). The plague was sustained and promoted by the prevailing conditions it encountered – dense population, high human mobility and poor hygiene environments (Cornelia Knab, cited in Meiklejohn). Eventually the plague reached Peking and as far as central China
In the disease’s wake mortality proceeded at an alarming rate, Harbin in the far north was the initial epicentre. In November 5,272 died in the city. It then spread along the tracks to cities further south, Mukden recorded a death toll of 2,571 by January 1911, and Changchun was losing over 200 a day to the plague (Meiklejohn). The plague was sustained and promoted by the prevailing conditions it encountered – dense population, high human mobility and poor hygiene environments (Cornelia Knab, cited in Meiklejohn). Eventually the plague reached Peking and as far as central China〲.
Enter Dr Wu
The authorities, in desperation, turned to a migrant, Penang-born doctor working at the time in Tianjin, Wu Lien-Teh. Cambridge-educated Wu took immediate charge of the medical emergency in Harbin. Enforcing a strict quarantine in the city, Wu put in place a series of comprehensive measures to contain the disease, including:
● converting railway freight cars to makeshift quarantine centres and turning a bathing establishment into a plague hospital
● establishing “sanitary zones” in the city
● closing down the railways in Manchuria, impose blockades, border controls and so stop infected people from travelling (Wu needed to secure the co-operation of the Russian and Japanese rail companies to achieve this)
● burning the lodgings of those infected
● monitoring the population by checking households for new cases
● advocating the wearing of face masks (Wu had more effective masks with extra gauze padding made)
● carrying out mass cremations of the infected dead (considered a sacrilege in Chinese society, Wu had to petition the emperor for permission)✪
● undertaking post-mortem examinations of the victims (again, a Chinese taboo that Wu had to overcome objections to)✲
Temperature check, Fuchiatien ⟱
(www.Flickr.com)

With no vaccine for pneumatic plague available, Wu’s quarantine measures involved isolating people for a five to ten day period, if no symptoms present, they are released with a wire band attached to their wrist signifying they have been cleared of the disease [‘In 1911, another epidemic swept through China. That time, the world came together’, (Paul French), CNN, 19-Apr-2020, www.cnn.com; ‘The Chinese Doctor Who Beat the Plague’, (Jeremiah Jenne), China Channel, 20-Dec-2018, www.chinachannel.org].
⟱ Old plague hospital, Harbin. When the epidemic was suppressed, the hospital was burnt down to eliminate any residual risk of contamination

(Photo: www.avezink.livejournal.com)
Keeping the ports plague-free
The concerted efforts of Japanese, Russian and Chinese managed to prevent the epidemic from reaching the eastern seaboard. Several towns close to the major port city Dalian reported cases, but Dalian itself (by this time under Japanese control, known as Dairen), initially undertook mass inspections of train and ship passengers, before closing the South Manchurian line altogether. With such strictures in place Dalian was wholly spared from the plague (French). The Russians were able to similarly stem the outbreak’s movement along the CER rail line and stop it from reaching Russia’s vital Pacific port, Vladivostok.
Racing against catastrophe
What added even more pressure to Wu’s task in trying to control the plague was that he was working against a tight deadline. The plague needed to be contained before 30th January which was Chinese New Year’s Eve. Thousands of migrant workers would be returning home to their families for this most important annual celebrations in China via the Manchurian railway network, which Wu knew would make it almost impossible to rein in the outbreak. The conscientious and thorough measures implemented in northern China made it possible for Wu to be able to declare the epidemic virtually suppressed by the end of January. Decisive action in N.E. China also prevented the plague from spreading to near-by (Outer) Mongolia and Russian Siberia. By March all the region’s shops, factories and schools were reopened and the only lingering infection was confined within the specially established plague hospitals (Meiklejohn).

Endnote: Dr Wu
Many Chinese medical personnel including epidemiologists and other physicians contributed to preventing the plague spreading throughout China, and to suppressing it all together within a short period. But if anyone should be called a hero of the Great Manchurian Plague of 1910-11, certainly that mantle should land on Dr Wu Lien-Teh, whose decisive leadership, organisation and enterprise saved China’s North-East provinces from a much higher casualty toll and from the regional plague developing into a nationwide epidemic.
꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙꧙
⌖ China for it’s part controlled the Imperial Railways of North China, which linked Peking with Mukden
〲 one case was recorded in Shanghai, 2,000 miles away
✪ thousands of bodies were still above ground in coffins because the relatives were waiting for the spring thaw to bury the dead…ideal incubators for the plague bacillus to magnify the contamination [‘Dr Wu Lien-Teh, plague fighter and father of the Chinese public health system’, (Zhongliang Ma & Yanli Li), www.ncbi.nim.nih.gov; Jenne)
✲ Wu performed the first autopsy in Harbin, identifying the disease as the bacterium Yersinia pestis of the pneumonic variant [‘Wu Lieh-Teh: Malaysia’s little-known plague virus fighter’, Star Online, 11-Feb-2020, www.msn.com]












 (Map image: www.eurogeologists.eu)
(Map image: www.eurogeologists.eu) A Chinese market trader in Vladivostok (Photo: AFP)
A Chinese market trader in Vladivostok (Photo: AFP)  New ‘besties’ Xi and Putin toast one another (Photo: AP)
New ‘besties’ Xi and Putin toast one another (Photo: AP)
 〨 Heihe, Chinese boomtown in Dong-Bei region
〨 Heihe, Chinese boomtown in Dong-Bei region